SCIENTIFIC REPORTS
Source - Archaeology: Occupational hazards for ancient | EurekAlert!
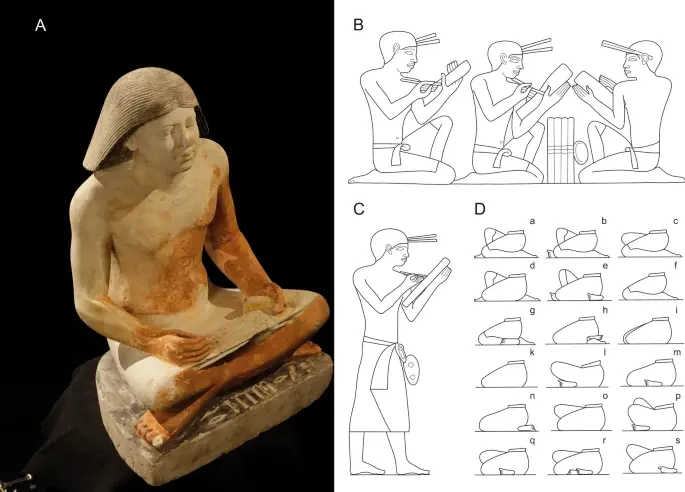 Working positions of scribes. (A) cross-legged (sartorial) position (the scribal statue of the high-ranking dignitary Nefer, Abusir; photo Martin Frouz); (B) kneeling-squatting position (wall decoration from the mastaba of the dwarf Seneb29); (C) standing position (wall decoration from the mastaba of the dwarf Seneb29); (D) based on tomb relief decoration, different position of the legs when sitting30. Drawing Jolana Malátková.
Working positions of scribes. (A) cross-legged (sartorial) position (the scribal statue of the high-ranking dignitary Nefer, Abusir; photo Martin Frouz); (B) kneeling-squatting position (wall decoration from the mastaba of the dwarf Seneb29); (C) standing position (wall decoration from the mastaba of the dwarf Seneb29); (D) based on tomb relief decoration, different position of the legs when sitting30. Drawing Jolana Malátková.
Repetitive tasks carried out by ancient Egyptian scribes — high status men with the ability to write who performed administrative tasks — and the positions they sat in while working may have led to degenerative skeletal changes, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Petra Brukner Havelková and colleagues examined the skeletal remains of 69 adult males — 30 of whom were scribes — who were buried in the necropolis at Abusir, Egypt between 2700 and 2180 BCE. They identified degenerative joint changes that were more common among scribes compared to men with other occupations. These were in the joints connecting the lower jaw to the skull, the right collarbone, the top of the right humerus (where it meets the shoulder), the first metacarpal bone in the right thumb, the bottom of the thigh (where it meets the knee), and throughout the spine, but particularly at the top. The authors also identified bone changes that could be indicative of physical stress caused by repeated use in the humerus and left hip bone, which were more common among scribes than men with other occupations. Other skeletal features that were more common among scribes were an indentation on both kneecaps and a flattened surface on a bone in the lower part of the right ankle.
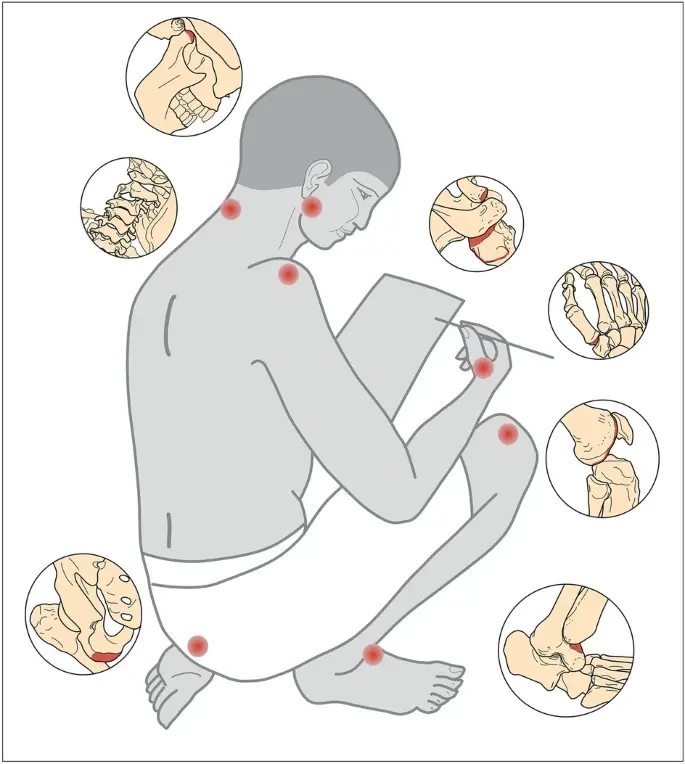 Drawing indicating the most affected regions of the skeletons of scribes with higher prevalence of evaluated changes compared to reference group: both temporomandibular joints (OA); cervical spine (OA, spondylosis); right shoulder (OA of the acromial facet of the clavicle and humeral head, EC on the greater tubercle of the humerus); right first metacarpal bone (OA); left ischial tuberosity (EC); right femoral medial condyle (OA) and the medial squatting facet on the right talus. Drawing Jolana Malátková.
Drawing indicating the most affected regions of the skeletons of scribes with higher prevalence of evaluated changes compared to reference group: both temporomandibular joints (OA); cervical spine (OA, spondylosis); right shoulder (OA of the acromial facet of the clavicle and humeral head, EC on the greater tubercle of the humerus); right first metacarpal bone (OA); left ischial tuberosity (EC); right femoral medial condyle (OA) and the medial squatting facet on the right talus. Drawing Jolana Malátková.
The authors suggest that the degenerative changes observed in the spines and shoulders of scribes could result from them sitting for prolonged periods in a cross-legged position with the head bent forwards, the spine flexed, and their arms unsupported. However, changes to knees, hips, and ankles could indicate that scribes may have preferred to sit with the left leg in a kneeling or cross-legged position and the right leg bent with the knee pointing upwards (in a squatting or crouching position). The authors note that statues and wall decorations in tombs have depicted scribes sitting in both positions, in addition to standing, while working. Degeneration to the jaw joints could have resulted from scribes chewing the ends of rush stems to form brush-like heads they could write with, while degeneration to the right thumb could have been caused by repeatedly pinching their pens.
The findings provide greater insight into the lives of scribes in ancient Egypt during the third millennium BCE.
Ancient Egyptian scribes and specific skeletal occupational risk markers (Abusir, Old Kingdom) DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63549-z